| Last week our kitchen ceiling fan and light combo decided to stop working. We don’t like eating in the dark, so I was compelled to do some immediate troubleshooting. As an engineer with training in the workings of electricity I have a great respect for it. I’m well aware of potential hazards, and I took a necessary precaution before taking things apart and disconnecting wires. I made the long haul down the stairs to the basement, opened the circuit breaker in the electrical panel, and disabled the flow of electricity to the kitchen. My fears of potential electrocution having been eliminated, my only remaining fear was of tumbling off the ladder while servicing the fan.
Just as I took the precaution to disconnect the power supply before performing electrical maintenance in my home, workers in industrial settings must do the same, and a chief player in those scenarios is the motor overload relay discussed last week. It automatically shuts down electric motors when they become overheated. Let’s revisit that example now. Figure 1
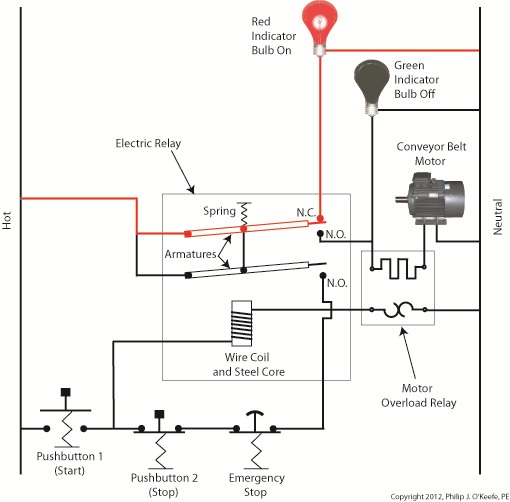
Our diagram in Figure 1 shows electric current flowing through the circuit by way of the red path. Even if this line were shut down, current would continue to flow along the path, because there is no means to disconnect the entire control system from the hot and neutral lines supplying power to it, that is, it is missing disconnect switches. Electric current will continue to pose a threat to workers were they to attempt a repair to the system. Now let’s see how we can eliminate potential hazards on the line. Figure 2
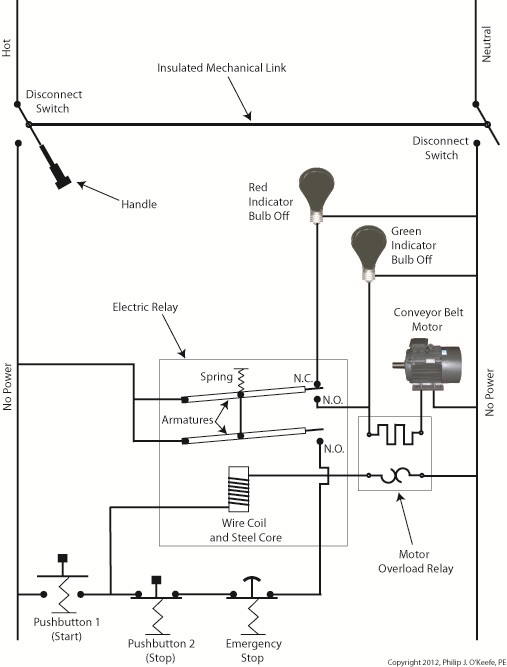
In Figure 2 there is an obvious absence of the color red, indicating the lack of current within the system. We accomplished this with the addition of disconnect switches capable of isolating the motor control circuitry, thereby cutting off the hot and neutral lines of the electrical power supply and along with it the unencumbered flow of electricity. These switches are basically the same as those seen in earlier diagrams in our series on industrial controls, the difference here is that the two switches are tied together by an insulated mechanical link. This link causes them to open and close at the same time. The switches are opened and closed manually via a handle. When the disconnect switches are both open electricity can’t flow and nothing can operate. Under these conditions there is no risk of a worker coming along and accidentally starting the conveyor motor. To add yet another level of safety, disconnect switches are often tagged and locked once de-energized. This prevents workers from mistakenly closing them and starting the conveyor while maintenance is being performed. Brightly colored tags alert everyone that maintenance is taking place and the switches must not be closed. The lock that performs this safety function is actually a padlock. It’s inserted through a hole in the switch handle, making it impossible for anyone to flip the switch. Tags and locks are usually placed on switches by maintenance personnel before repairs begin and are removed when work is completed. Now let’s see how our example control system looks in ladder diagram format. Figure 3
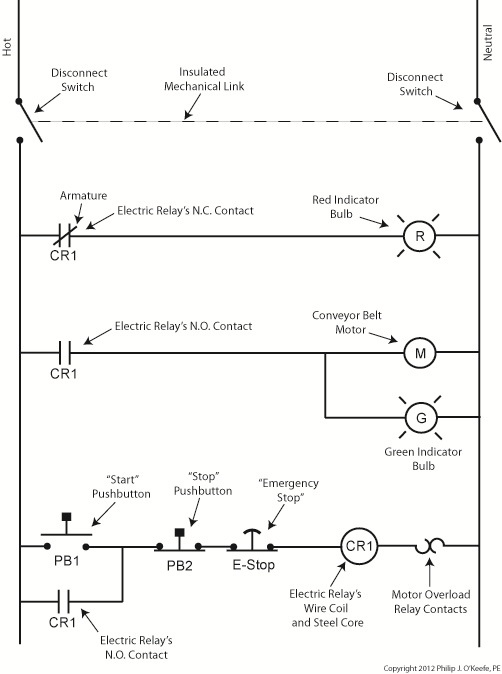
Figure 3 shows a ladder diagram that includes disconnect switches, an emergency stop button, and the motor overload relay contacts. The insulated mechanical link between the two switches is represented by a dashed line. Oddly enough, engineering convention has it that the motor overload relay heater is typically not shown in a ladder diagram, therefore it is not represented here. This wraps up our series on industrial control. Next time we’ll begin a discussion on mechanical clutches and how they’re used to transmit power from gasoline engines to tools like chainsaws and grass trimmers. ____________________________________________
|
Posts Tagged ‘hot’
Industrial Control Basics – Disconnect Switches
Sunday, March 25th, 2012Tags: chainsaw, circuit breaker, circuitry, clutch, control panel, conveyor belt, current flow, death, disconnect switch, electric motor, electric relay, electrical maintenance, electrical panel, electricity, electrocution, emergency stop, engineering expert witness, forensic engineer, hot, indicator bulbs, industrial control system, injury, lawn trimmer, lock, lockout tag out, maintenance worker, motor overheated, neutral, overload relay, overload relay heater, potential hazards, power supply, pushbutton, safety, safety hazard, tag, troubleshooting, wires
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | Comments Off on Industrial Control Basics – Disconnect Switches
Industrial Control Basics – Motor Overload Relay In Action
Sunday, March 18th, 2012|
Last week we explored the topic of thermal expansion, and we learned how the bimetal contacts in a motor overload relay distort when heated. We also discussed how the overload relay comes into play to prevent overheating in electric motor circuits. Now let’s see what happens when an overload situation occurs. Figure 1
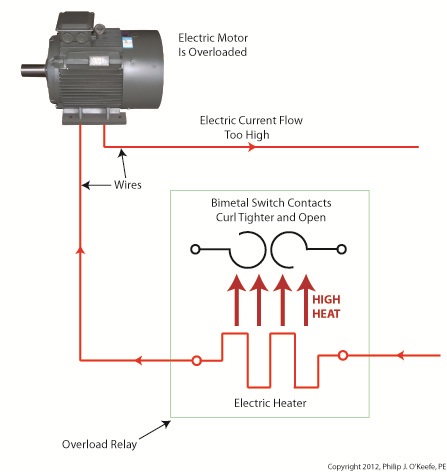
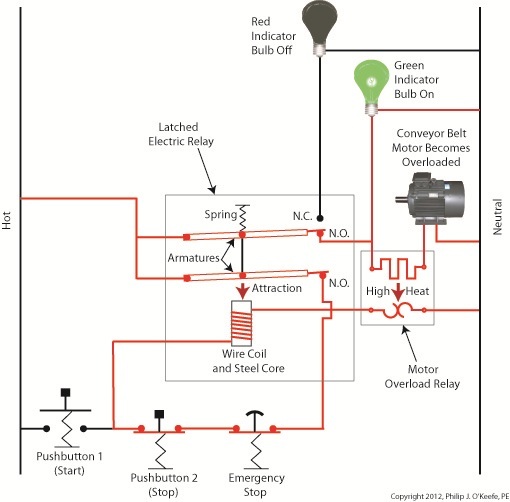
Figure 1 shows a motor becoming overloaded, as it draws in abnormally high amounts of electric current. Since this current also flows through the electric heater in the overload relay, the heater starts producing more heat than it would if the motor were running normally. This abnormally high heat is directed towards the bimetal switch contacts, causing them to curl up tightly until they no longer touch each other and open up. They will only close again when the overload condition is cleared up and the heater cools back down to normal operating temperature. Let’s now take a look at Figure 2 to see how the motor overload relay fits into our example of a conveyor belt motor control circuit. Once again, the path of electric current flow is denoted by red lines. Figure 2
The circuit in Figure 2 represents what happens after Button 1 is depressed. That is, the electric relay has become latched and current flows between hot and neutral sides through one of the N.O. contacts along the path of the green indicator bulb, the motor overload relay heater, and the conveyor belt motor. The current also flows through the other N.O. contact, the Emergency Stop button, Button 2, the electric relay’s wire coil, and the motor overload relay bimetal contacts. The motor becomes overloaded, causing the overload relay heater to produce abnormally high heat. This heat is directed towards the bimetal contacts, also causing them to heat up. Figure 3
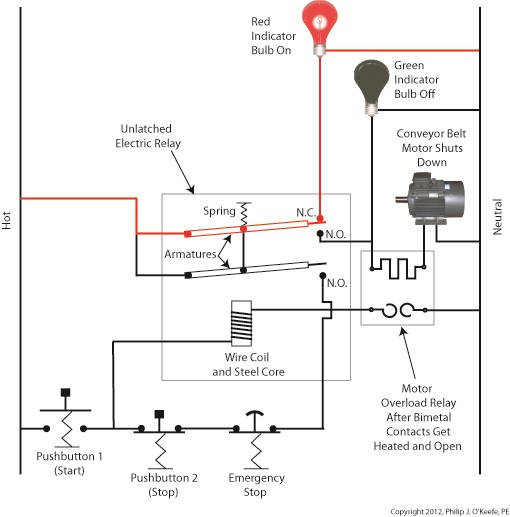
In Figure 3 the bimetal contacts have heated to the point that they have curled away from each other until they no longer touch. With the bimetal contacts open, electric current is unable to flow through to the electric relay’s wire coil. This in turn ends the magnetic attraction which formerly held the relay armatures against the N.O. contacts. The spring in the electric relay has pulled the armatures up, causing the N.O. contacts to open, simultaneously closing the N.C. contact. These actions have resulted in a loss of current to the green indicator bulb and electric motor. The red indicator bulb is now activated, and the conveyor motor is caused to automatically shut down to prevent damage and possible fire due to overheating. This means that even if the conveyor operator were to immediately press Button 1 in an attempt to restart the line, he would be prevented from doing so. Under these conditions the electric relay is prevented from latching, and the motor remains shut down because the bimetal contacts have been separated, preventing current from flowing through to the wire coil. The bimetal contacts will remain open until they once again cool to normal operating temperature. Once cooled, they will once again close, and the motor can be restarted. If the cause of the motor overload is not diagnosed and its ability to recur eliminated, the automatic shutdown process will repeat this cycle. Next time we’ll see how the overload relay is represented in a ladder diagram. We’ll also see how switches can be added to the circuit to allow maintenance staff to safely work. ____________________________________________
|
Tags: automatic control, bimetalic contacts, closed contact, controls engineer, electric current, electric relay, emergency stop, engineering expert witness, fire, forensic engineer, heater, hot, indicator bulb, industrial control, motor control, motor damage, motor overload, motor overload relay, N.C. contact, N.O. contact, neutral, normally closed contact, normally open contact, open contact, pushbutton
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | Comments Off on Industrial Control Basics – Motor Overload Relay In Action
Industrial Control Basics – Emergency Stops
Sunday, February 26th, 2012| Ever been in the basement when you heard a loud thud followed by a scream by a family member upstairs? You run up the stairs to see what manner of calamity has happened, the climb seeming to take an eternity. Imagine a similar scenario taking place in an industrial setting, where distances to be covered are potentially far greater and the dangerous scenarios numerous.
Suppose an employee working near a conveyor system notices that a coworker’s gotten caught in the mechanism. The conveyor has to be shut down fast, but the button to stop the line is located far away in the central control room. This is when emergency stop buttons come to the rescue, like the colorful example shown in Figure 1. Figure 1
Emergency stop buttons are mounted near potentially dangerous equipment in industrial settings, allowing workers in the area to quickly de-energize equipment should a dangerous situation arise. These buttons are typically much larger than your standard operational button, and they tend to be very brightly colored, making them stick out like a sore thumb. This type of notoriety is desirable when a high stress situation requiring immediate attention takes place. They’re easy to spot, and their shape makes them easy to activate with the smack of a nearby hand, broom, or whatever else is convenient. Figure 2 shows how an emergency stop button can be incorporated into a typical motor control circuit such as the one we’ve been working with in previous articles. Figure 2
An emergency stop button has been incorporated into the circuit in Figure 2. It depicts what happens when someone depresses Button 1 on the conveyor control panel. The N.C. contact opens, and the two N.O. contacts close. The motor starts, and the lit green bulb indicates it is running. The electric relay is latched because its wire coil remains energized through one N.O. contact. It will only become unlatched when the flow of current is interrupted to the wire coil, as is outlined in the following paragraph. The red lines denote areas with current flowing through them. Both Button 2 and the emergency stop button typically reside in normally closed positions. As such electricity will flow through them on a continuous basis, so long as neither one of them is re-engaged. If either of them becomes engaged, the same outcome will result, an interruption in current on the line. The relay wire coil will then become de-energized and the N.O. contacts will stay open, preventing the wire coil from becoming energized again after Button 2 or the emergency stop are disengaged. Under these conditions the conveyor motor stops, the green indicator bulb goes dark, the N.C. contact closes, and the red light comes on, indicating that the motor is not running. This sequence, as it results from hitting the emergency stop button, is illustrated in Figure 3. Figure 3
We now have the means to manually control the conveyor from a convenient, at-the-site-of-occurrence location, which allows for a quick shut down of operations should the need arise. So what if something else happens, like the conveyor motor overheats and catches on fire and no one is around to notice and hit the emergency stop? Unfortunately, in our circuit as illustrated thus far the line will continue to operate and the motor will continue to run unless we incorporate an additional safeguard, the motor overload relay. We’ll see how that’s done next time. ____________________________________________ |
Tags: control panel, control room, conveyor, de-energize equipment, electric relay, emergency pushbutton, emergency stop button, engineering expert witness, equipment shut down, fire, forensic engineer, hot, indicator bulb, industrial control, ladder diagram, latched relay, motor control, motor control circuit, motor overheat, N.C. contact, N.O. contact, NC contact, neutral, NO contact, overload relay, push button, pushbutton, relay armature, relay coil, relay ladder logic, safeguard, unlatched relay
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | 2 Comments »
Industrial Control Basics – Latching Circuit
Sunday, January 29th, 2012| When I think of latches the first thing that comes to mind is my Uncle Jake’s outhouse and how I got stuck in it as a kid. Its door was outfitted with a rusty old latch that had a nasty habit of locking up when someone entered, and it would take a tricky set of raps and bangs to loosen. One day it was being particularly unresponsive to my repeated attempts to open it, and the scene became like something out of a horror movie. There was a lot of screaming.
When latches operate well, they’re indispensable. Let’s take our example circuit from last time a bit further by adding more components and wires. We’ll see how a latch can be applied to take the place of pressure exerted by an index finger. See Figure 1. Figure 1
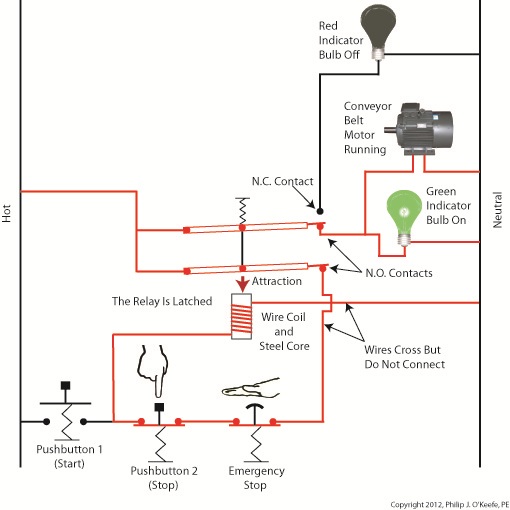
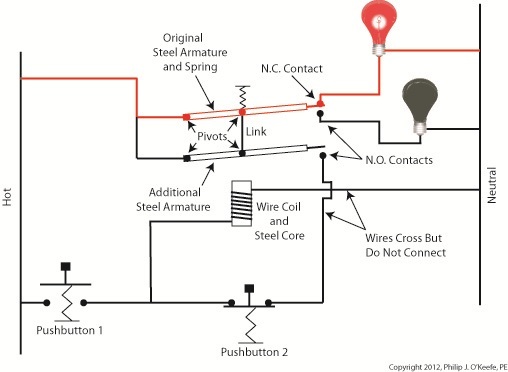
Our relay now contains an additional pivoting steel armature connected by a mechanical link to the original steel armature and spring. The relay still has one N.C. contact, but it now has two N.O. contacts. When the relay is in its normal state the spring holds both armatures away from the N.O. contacts so that no electric current will flow through them. One armature touches the N.C. contact, and this is the point at which current will flow between hot and neutral sides, lighting the red bulb. The parts of the circuit diagram with electric current flowing through them are denoted by red lines. Figure 1 reveals that there are now two pushbuttons instead of one. Now let’s go to Figure 2 to see what happens when someone presses on Button 1. Figure 2
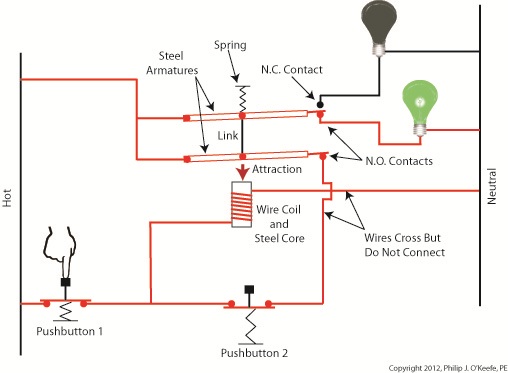
Again, the parts of the circuit diagram with current flowing through them are denoted by red lines. From this diagram you can see that when Button 1 is depressed, current flows through the wire coil, making it and its steel core magnetic. This electromagnet in turn attracts both steel armatures in our relay, causing them to pivot and touch their respective N.O. contacts. Electric current now flows between hot and neutral sides, lighting up the green bulb. Current no longer flows through the N.C. contact and the red bulb, making it go dark. If you look closely at Figure 2, you’ll notice that current can flow to the wire coil along two paths, either that of Button 1 or Button 2. It will also flow through both N.O. contact points, as well as the additional armature. So how is this scenario different from last week’s blog discussion? That becomes evident in Figure 3, when Button 1 is no longer depressed. Figure 3
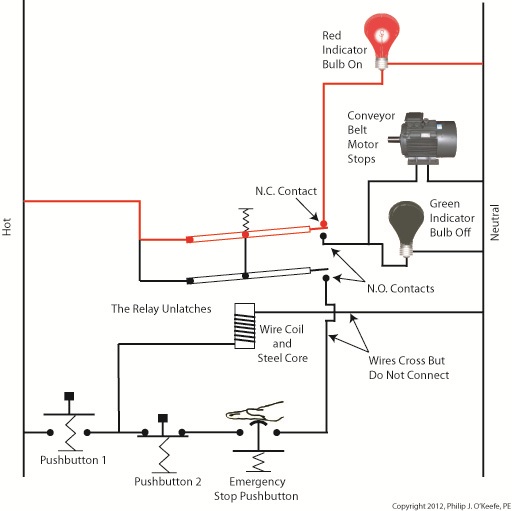
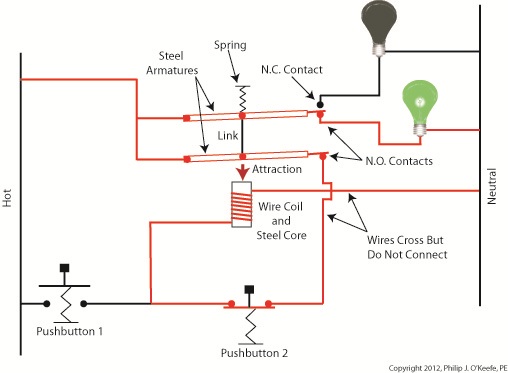
In Figure 3 Button 1 is not depressed, and electric current does not flow through it. The red bulb remains dark, and the green bulb lit. How can this state exist without the human intervention of a finger depressing the button? Because although one path for current flow was broken by releasing Button 1, the other path through Button 2 remains intact, allowing current to continue to flow through the wire coil. This situation exists because Button 2’s path is “latched.” Latching results in the relay’s wire coil keeping itself energized by maintaining armature contact at the N.O. contact points, even after Button 1 is released. When in the latched state, the magnetic attraction maintained by the wire coil and steel core won’t allow the armature to release from the N.O. contacts. This keeps current flowing through the wire coil and on to the green bulb. Under these conditions the relay will remain latched. But, just like my Uncle’s outhouse door, the relay can be unlatched if you know the trick to it. Relays may be latched or unlatched, and next week we’ll see how Button 2 comes into play to create an unlatched condition in which the green bulb is dark and the red bulb lit. We’ll also see how it is all represented in a ladder diagram. ____________________________________________ |
Tags: armature, automatic controls, controls engineer, electric current, electric relay, electrical contacts, electromagnet, engineering expert witness, forensic engineer, hot, industrial control, ladder diagram, latched relay, N.C. contact, N.O. contact, NC contact, neutral, NO contact, normal state, normally closed, normally open, pushbutton, relay, relay ladder logic, unlatched relay, wire, wire coil
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | Comments Off on Industrial Control Basics – Latching Circuit
Industrial Control Basics – Electric Relay Ladder Diagram
Sunday, January 22nd, 2012| My daughter will be studying for her driver’s license exam soon, and I can already hear the questions starting. “What does that sign mean? Why does this sign mean construction is ahead?” Symbols are an important part of our everyday lives, and in order to pass her test she’s going to become familiar with dozens of them that line our highways.
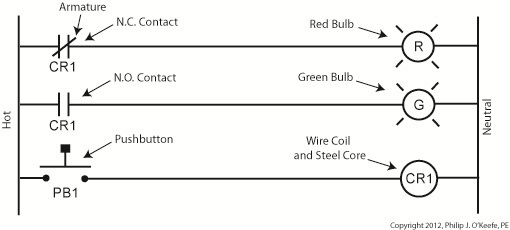
Just as a triangle on the highway is a symbol for “caution,” industrial control systems employ a variety of symbols in their diagrams. The pictures are shorthand for words. They simplify the message, just as hieroglyphics did for our early ancestors who had not yet mastered the ability to write. Ladder diagrams and the abstract symbols used in them are unique to industrial control systems, and they result in faster, clearer interpretations of how the system operates. Last week we analyzed an electric circuit to see what happens when we put a relay to use within a basic industrial control system, as found in Figure 1. Figure 1Now let’s see how it looks in an even simpler form, the three-rung ladder diagram shown in Figure 2. Figure 2In industrial control terminology the electric relays shown in ladder diagrams are often called “control relays,” denoted as CR. Since a ladder diagram can typically include many different control relays, they are numbered to avoid confusion. The relay shown in Figure 2 has been named “CR1.” Our ladder diagram contains a number of symbols. The symbol on the top rung which looks like two parallel vertical lines with a diagonal line bridging the gap between them represents the N.C. contact. This symbol’s vertical lines represent an air gap in the N.C. contact, the diagonal line is the relay armature which performs the function of bridging/closing the air gap. This rung of the ladder diagram represents the contact when the relay is in its normal state. In the middle ladder rung the N.O. contact symbol looks like two parallel vertical lines separated by a gap. There is no diagonal line running through it since the relay armature doesn’t touch the N.O. contact when this particular relay is in its normal state. The wire coil and steel core of this relay are represented by a circle on the bottom ladder rung. The contact and coil symbols on all three rungs are labeled “CR1” to make it clear that they are part of the same control relay. Other symbols within Figure 2 represent the red and green bulbs we have become familiar with from our initial illustration. They are depicted as circles, R for red and G for green, with symbolic light rays around them. The pushbutton, PB1, is represented as we have discussed in previous articles on ladder diagrams. Just as road sign symbols are faster than sentences for drivers speeding down a highway to interpret, ladder diagrams are faster than customary illustrations for busy workers to interpret. Next time we’ll expand on our electric relay by introducing latching components into the control system that will allow for a greater degree of automation. ____________________________________________ |
Tags: armature, automation engineer, bulb, contact, control relay, controls engineer, CR, electric relay, electrical contact, engineering expert witness, forensic engineer, hot, industrial automation, industrial control, ladder diagram, ladder diagram symbol, ladder logic, N.C. contact, N.O. contact, NC contact, neutral, NO contact, normal state, normally closed, normally open, pushbutton, relay, rung, steel core, wire coil
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | 2 Comments »
Industrial Control Basics – Electric Relay Example
Saturday, January 14th, 2012| When a starving monkey is faced with two buttons, one representing access to a banana, the other cocaine, which will he push? The cocaine, every time. The presence of buttons usually indicates a choice must be made, and electric relays illustrate this dynamic.
Last week we looked at a basic electric relay and saw how it was used to facilitate a choice in electricity flow between two paths in a circuit. Now let’s see what happens when we put a relay to use within a basic industrial control system making use of lit bulbs. Figure 1
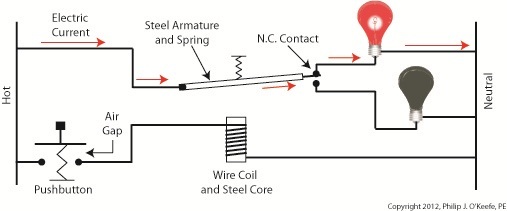
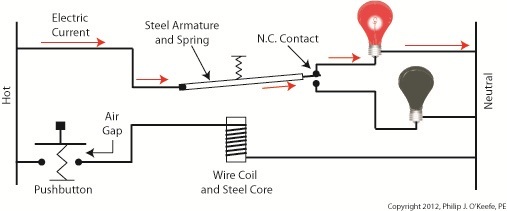
Figure 1 shows an electric relay that’s connected to both hot and neutral wires. At the left side is our pushbutton and the hot wire, on the right two bulbs, one lit, one not, and the neutral wire. No one is depressing the pushbutton, so an air gap exists, preventing current from flowing through the wire coil between the hot and neutral sides. With these conditions in place the relay is said to be in its “normal state.” The relaxed spring positioned on the relay armature keeps it touching the N.C. contact. This allows current to flow between hot and neutral through the armature and the N.C. contact. When these conditions exist the red bulb is lit, and this is accomplished without the need for anyone to throw a switch or press a button. In this condition the other lamp will remain disengaged and unlit. Now let’s refer to Figure 2 to see what happens when someone presses the button. Figure 2
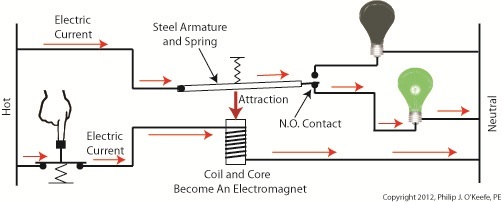
When the button is depressed the air gap is eliminated and the coil and wire become magnetized. They will attract the steel armature closer to them, the spring to expand, and the armature to engage with the N.O. contact. Under these conditions current will no longer flow along a path to light the red bulb because an air gap has been created between the armature and N.C. contact. The current instead flows through the N.O. contact, lighting the green bulb. It will stay lit so long as someone holds the button down. If our monkey were faced with the scenarios presented in Figures l and 2 and a banana was placed in the position of the red bulb, the cocaine in the position of the green, he might find that the regular delivery of bananas that takes place when the relay is in the N.C. contact position is enough to keep him happy. In this state he might be so full of bananas he won’t want to expend the energy to engage the button into the N.O. contact position for the delivery of cocaine. Next time we’ll revisit the subject of ladder diagrams and see how they are used to denote the paths of electric relays. ____________________________________________ |
Tags: armature, bulb, coil, electric circuit, electric current, electric relay example, electricity flow, electro-mechanical relay, electromagnet, engineering expert witness, forensic engineer, hot, hot wire, industrial control, lamp, N.C. contact, N.O. contact, NC contact, neutral, neutral wire, NO contact, normal state, normally closed contact, normally open contact, pushbutton, relay, spring, switch, wire coil
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | 1 Comment »
Industrial Control Basics – Pushbuttons
Monday, December 26th, 2011Tags: control system, current flow, electric motor, electrical circuit, engineering expert witness, forensic engineer, hot, industrial control, ladder diagram, machine control, mechanized equipment, motor control, neutral, normally closed, normally open, pushbutton, relay, spring, switch
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | Comments Off on Industrial Control Basics – Pushbuttons
Industrial Control Basics – Ladder Diagrams
Sunday, December 18th, 2011| The other day I pressed the button to activate my electric garage door opener and nothing happened. I pushed again and again, still nothing. Finally, I convinced myself to get out of the car and take a closer look. A wooden board I had propped up against the side of the garage wall had come loose, wedging itself in front of the electric eye, you know, the one that acts as a safety. The board was an obstruction to the clear vision of the eye. It couldn’t see the light emitter on the other side of the door opening and wouldn’t permit the door opener to function.
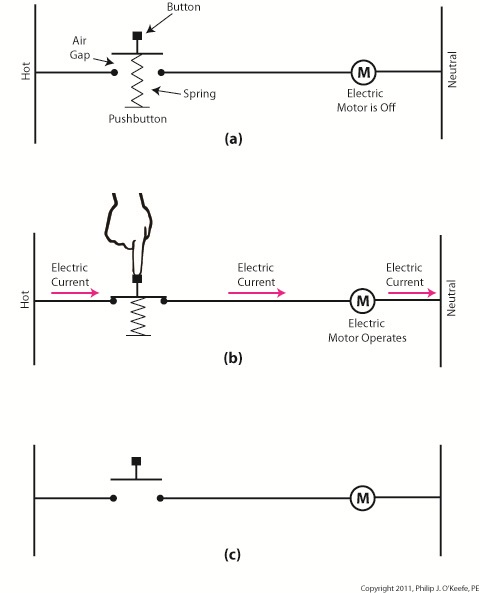
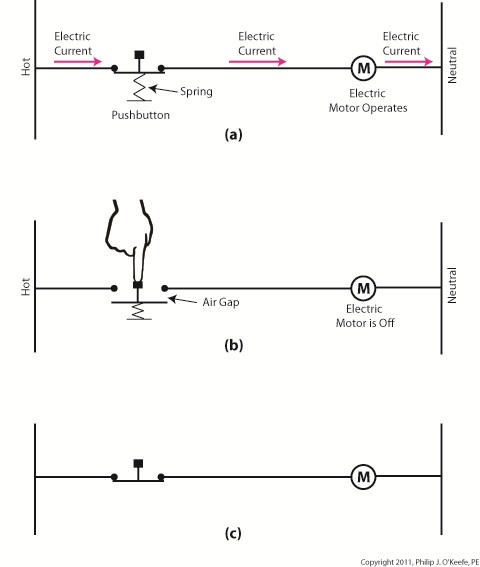
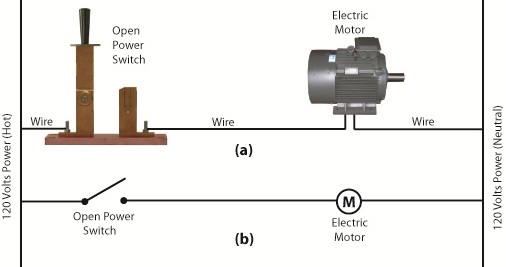
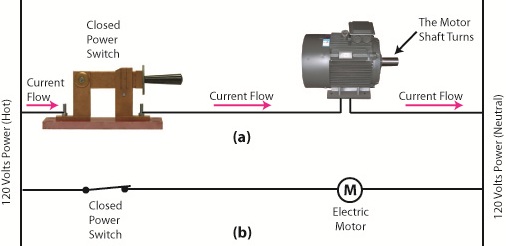
The basic manual control system we looked at last week operates similarly to the eye on a garage door opener. If you can’t “close the loop,” you won’t get the power. Last week’s example was as basic as things get. Now let’s look at something a bit more complex. Words aren’t always the best vehicle to facilitate understanding, which is why I often use visual aids in my work. In the field of industrial control systems diagrams are often used to illustrate things. Whether it’s by putting pencil to paper or the flow diagram of software logic, illustrations make things easier to interpret. Diagrams such as the one in Figure l are often referred to as “ladder diagrams,” and in a minute we’ll see why. Figure 1 Figure 1(a) shows a basic manual control system. It consists of wires that connect a power switch and electric motor to a 120 volt alternating current power source. One wire is “hot,” the other “neutral.” The hot side is ungrounded, meaning that it isn’t electrically connected to the Earth. The neutral side is grounded, that’s right, it’s driven into the ground and its energy is dissipated right into the earth, then returned back to the power grid. In Figure 1(a) we see that the power switch is open and an air gap exists. When gaps exist, we don’t have a closed electrical loop, and electricity will not flow. Figure 1(b), our ladder diagram, aka line diagram, shows an easier, more simplified representation of the manual control shown in Figure 1(a). It’s easier to decipher because there’s less going on visually for the brain to interpret. Everything has been reduced to simple lines and symbols. For example, the electric motor is represented by a symbol consisting of a circle with an “M” in it. Now, let’s turn our attention to Figure 2 below to see what happens when the power switch is closed. Figure 2 The power switch in Figure 2(a) is closed, allowing electric current to flow between hot and neutral wires, then power switch, and finally to the motor. The current flow makes the motor come to life and the motor shaft begins to turn. The line diagram for this circuit is shown in Figure 2(b). You might have noticed that the line diagrams show in Figures 1(b) and 2(b) have a rather peculiar shape. The vertically running lines at either side depict the hot and neutral legs of the system. If you stretch your imagination a bit, they look like the legs of a ladder. Between them run the wires, power switch, and motor, and this horizontal running line represents the rung of the ladder. More complicated line diagrams can have hundreds, or even thousands of rungs, making up one humongous ladder, hence they are commonly referred to as ladder diagrams. Next week we’ll take a look at two key elements in automatic control systems, the push button and electric relay, elements which allow us to do away with the need for human intervention. ____________________________________________ |
Tags: automatic control, electric circuit, electric current, electric motor, electric relay, electric utility, engineering expert witenss, forensic engineer, ground, hot, industrial control, ladder diagram, ladder logic, line diagram, manual control, motor control, neutral, power flow, power grid, power switch, push button, visual aid, wires
Posted in Courtroom Visual Aids, Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Innovation and Intellectual Property, Personal Injury, Product Liability, Professional Malpractice | Comments Off on Industrial Control Basics – Ladder Diagrams
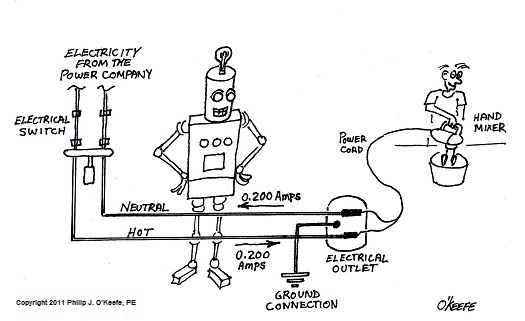
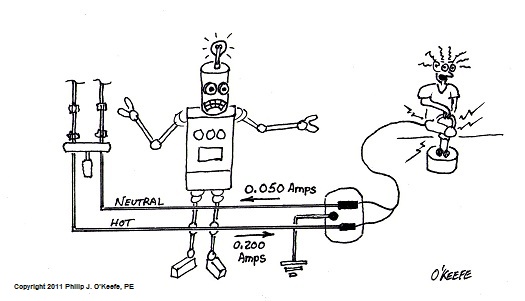
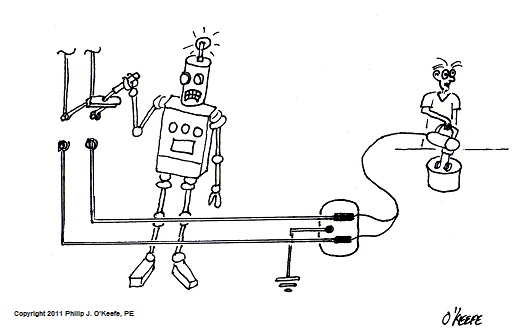
GFCI Outlets and The Mighty Robot
Sunday, July 3rd, 2011Tags: appliance, current flow, Discovery Channel, electrical switch, electrocution, electron flow, engineering expert witness, forensic engineer, GFCI, ground, ground fault, ground fault circuit interrupter, hand mixer, hot, neutral, plug, shock hazard, wall outlet
Posted in Engineering and Science, Expert Witness, Forensic Engineering, Personal Injury, Product Liability | Comments Off on GFCI Outlets and The Mighty Robot