|
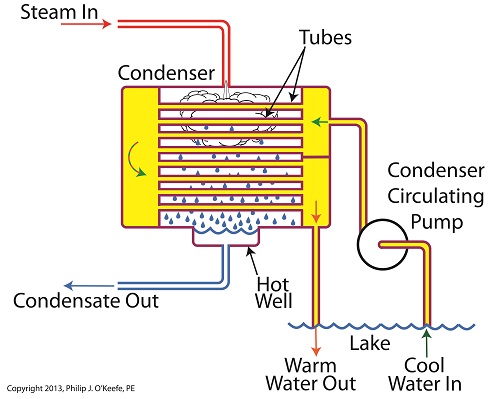
Winter is fast approaching. Imagine living in a house without insulation. Now imagine your heating bill, which will be high due to the tremendous amount of heat loss. Energy is a precious resource, no matter how it’s produced, and its conservation within a power plant’s steam/water cycle is of vital importance. Last time we learned about the transfer of heat energy within a power plant’s condenser, where some of the heat energy contained within its steam is absorbed by the cool lake water contained inside its tubes. Steam is continuously flowing into the condenser from the steam turbine, so it’s essential for the circulating pump to keep a fresh supply of lake water flowing through the condenser’s tubes in an effort to keep temperatures under control. The compensating action that’s provided by the cool lake water flowing within the tubes, represented by green arrows in the illustration, keeps the temperature inside the tubes from rising and becoming equal to the steam’s temperature outside of them. If the flow of cool water through the tubes were to stop and the temperatures inside and outside the tubes become equal, the water contained inside the tubes would boil off to steam, resulting in the tubes bursting and a wrecked condenser. After absorbing heat energy from the surrounding steam, the warmed lake water within the tubes follows a circuitous path through the tubing, eventually emptying out into the lake. The orange arrows in the illustration show this path. Okay, with this warm water entering the lake, doesn’t that harm the eco system? Actually its impact is negligible. You see, the temperature of the lake water leaving the condenser is only about 10°F higher than when it was pumped from the lake. Add this to the fact that the volume of water contained within a lake is huge in comparison to the small amount of warmed water being returned to it. Next week we’ll see how the loss of heat energy affects the steam, and how an important part of the condenser known as the hot well comes into play. ________________________________________ |
Tags: coal power plant, coal power plant engineering, condenser, condenser circulating pump, condenser tubes, condenser vessel, cooling water, electric utility power plant training, expert witness, forensic engineer, heat energy, lake water, steam turbine, thermal engineering, turbine exhaust steam