|
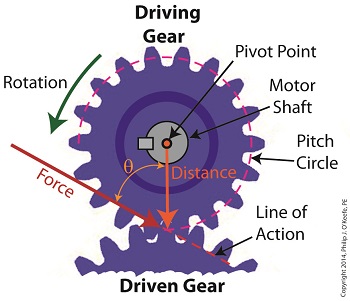
We’ve been discussing torque and how it enables more power to be available to applications such as loosening tight nuts with a wrench. Now we’ll see how those same principles apply to another application, a simple gear train. To review, the torque formula is, Torque = Distance × Force × sin(ϴ) where, Distance and Force are vector magnitudes and ϴ is the angle formed between them. Referring to the gear train illustration above, we see that Force and Distance vectors are present, just as they had been in our previous wrench/nut example. But instead of torque being created by way of force that’s applied to a wrench, things are reversed, and it’s the torque that creates the force. You see, in the wrench/nut example, the force applied to the wrench handle created torque on the nut. In our present gear train example, the torque applied to the motor shaft is created by an electric motor exerting pressure upon the motor shaft, which in turn exerts a force upon the driving gear teeth. The driving gear is also attached to this shaft, so torque causes the driving gear to rotate along with the motor. This rotation results in a force being exerted at the point where the teeth of the driving gear mesh with the teeth of the driven gear. In other words, in the wrench/nut example force created torque, while in the present example torque creates a force. The gear train has a pivot point, as there was in our wrench/nut example, but this time it’s located at the center of the motor shaft rather than at the center of a nut. The pivot point in both examples is where the action takes place. The motor’s shaft and driving gear rotate around it, just as the wrench jaws and handle rotated around the nut’s pivot point. In both examples, the Distance vectors extend out from the pivot points to meet up with the Force vector’s path. In the gear train example, this Force vector path is called a line of action, as introduced earlier in this blog series. This line of action passes through to the point where the driving and driven gear teeth mesh. The force acting upon that point causes the gears in the gear train to rotate, and as they turn mechanical energy is transferred from the motor to whatever machinery component is attached to the shaft of the driven gear. The powered component will then be able to perform useful work such as cutting lumber, mixing frosting for a cake, drilling holes in steel, or propelling vehicles. You will note that there is an angle ϴ which exists between the Distance and Force vectors. Since we have a pivot point, a Force vector, a Distance vector, and an angle ϴ, we are able to apply the torque formula to gear trains exactly as we did in our wrench/nut example. We can then use that formula to calculate how torque is transmitted between gears in the train. Next time we’ll examine the distance and force vectors in a simple gear train. _______________________________________ |
Archive for April, 2014
Torque and Force
Tuesday, April 29th, 2014Manipulating theTorque Formula
Wednesday, April 23rd, 2014|
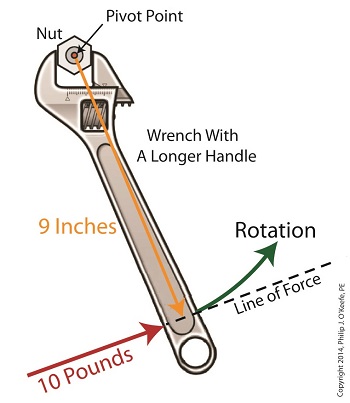
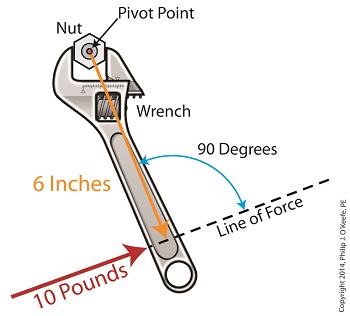
Last time we introduced the simplified formula for torque: Torque = Distance × Force Today we’ll manipulate it by way of our wrench and nut example to get the torque that we need to loosen a tight nut. By inserting the numerical values of our illustration into the torque formula, it becomes: Torque = 6 inches × 10 pounds = 60 inch-pounds Inch-pounds may be terminology you’re unfamiliar with, but this notation arises from the fact that torque values are always represented by units of distance and force separated by a hyphen, in our case inch-pounds. This just means that distance and force were multiplied together to calculate torque. In order to manipulate the value for torque all that needs to be done is change either or both numerical values for Distance and Force. Increasing either or both factors produces higher torque, decreasing them less torque. Why manipulate torque? To provide us with a mechanical advantage. Suppose we have a rusted nut that we’re trying to move with a wrench that has a 6 inch handle, and the 10 pounds of force employed by the muscles in our arm just won’t budge it. Put another way, 60 inch-pounds of torque is insufficient to rotate the nut. It’s clear we must increase torque to get things going. Let’s do so by increasing either of the vector magnitudes. First we’ll try increasing the magnitude of the force vector. Instead of simply pushing hard on the wrench handle with our arm, let’s say we push extra hard. The average man can do a bicep curl of between 30 to 40 pounds, but we haven’t been going to the gym lately and we’re really out of shape. So try as we will, we just can’t muster up the bicep strength to apply more than 10 pounds of force to the wrench handle. It’s clear that this approach to increasing torque upon the nut isn’t going to work. The other way to increase torque is to increase the length of the distance vector. We’ll need a wrench with a longer handle, say 9 inches. By using a wrench with a longer handle we have increased the magnitude of the distance vector from 6 to 9 inches. The torque formula becomes: Torque = 9 inches × 10 pounds = 90 inch-pounds Eureka! The longer handle has provided us with the mechanical advantage needed to increase torque to 90 inch-pounds, thereby overcoming our muscular shortcomings and breaking the nut free. In summary, since torque is the product of the magnitudes of the distance and force vectors, we can increase torque by either increasing the magnitude of the force vector, or as in our example, by increasing the magnitude of the distance vector. Next time we’ll see how to apply the principles of torque to a real world situation involving gear trains in which we need to obtain a mechanical advantage. _______________________________________ |
Torque Formula Symplified
Wednesday, April 2nd, 2014|
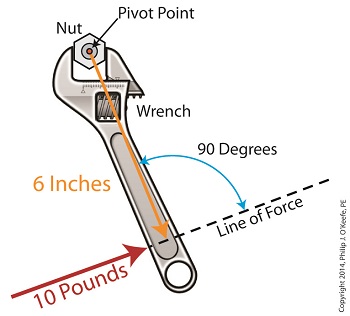
Last time we introduced the mathematical formula for torque, which is most simply defined as a measure of how much a force acting upon an object causes that object to rotate around a pivot point. When manipulated, torque can produce a mechanical advantage in gear trains and tools, which we’ll see later. The formula is: Torque = Distance × Force × sin(ϴ) We learned that the factors Distance and Force are vectors, and sin(ϴ) is a trigonometric function of the angle ϴ which is formed between their two vectors. Let’s return to our wrench example and see how the torque formula works. Vectors have both a magnitude, that is, a size or extent, and a direction, and they are typically represented in physics and engineering problems by straight arrows. In our illustration the vector for distance is represented by an orange arrow, while the vector for force is represented by a red arrow. The orange distance vector has a magnitude of 6 inches, while the red force vector has a magnitude of 10 pounds, which is being supplied by the user’s arm muscle manipulating the nut. That muscle force follows a path from the arm to the pivot point located at the center of the nut, a distance of 6 inches. Vector arrows point in a specific direction, a direction which is indicative of the way in which the vectors’ magnitudes — in our case inches of distance vs. pounds of force — are oriented with respect to one another. In our illustration the orange distance vector points away from the pivot point. This is according to engineering and physics convention, which dictates that, when a force vector is acting upon an object to produce a torque, the distance vector always points from the object’s pivot point to the line of force associated with the force vector. The angle, ϴ, that is formed between the two vectors in our example is 90 degrees, as measured by any common, ordinary protractor. Next we must determine the trigonometric value for sin(ϴ). This is easily accomplished by simply entering “90” into our calculator, then pressing the sin button. An interesting fact is that when the angle ϴ ranges anywhere between 0 and 90 degrees, the values for sin(ϴ) always range between 0 and 1. To see this in action enter any number between 0 and 90 into a scientific calculator, then press the sin button. For our angle of 90 degrees we find that, sin(90) = 1 Thus the formula for torque in our example, because the sin(ϴ) is equal to 1, simply becomes the product of the magnitudes of the Distance and Force vectors: Torque = Distance × Force × sin(90) Torque = Distance × Force × 1 Torque = Distance × Force Next time we’ll insert numerical values into the equation and see how easily torque can be manipulated. _______________________________________ |