|
Hold onto your hats, we’re going to deal with a lot of equations today! Last time we used flashbacks to previous blogs in this series to revisit key equations in our ongoing discussion of gear trains and torque. We also introduced The Law of Conservation of Energy in conjunction with five equations that together demonstrate how when increasing torque by use of a simple gear train, we do so at the cost of speed. Those five equations are:
where, R is the gear ratio, N the number of gear teeth, n the gear’s rotational speed, T the torque, D the gear pitch radius, and HP is the horsepower transmitted by the gears. As we work the equations, keep in mind that our ultimate objective is to find a way to link together (1) and (2), the equations dealing with gear torque and speed. Once we accomplish this we’ll see how increased torque is obtained at the cost of speed. But because there are no common terms between equations (1) and (2), our first step is to develop one. Developing a link between equations (1) and (2) is a process that begins with combining equations (2), (3), and (4).
The common terms in these three equations are TDriving and TDriven, so we’ll manipulate things in order to group them together. We’ll substitute equation (3) for the TDriving term in equation (2), and substitute equation (4) for the TDriven term in equation (2). We are now able to link all three equations to get: {[HPDriving ÷ nDriving] × 63,025} ÷ {[HPDriven ÷ nDriven] × 63,025} = DDriving ÷ DDriven (6) Now let’s go a step further to simplify equation (6). From equation (5) we know that the driving and driven gear horsepowers are equal. So, in equation (6), the HPDriving and HPDriven cancel out, along with the two 63,025 terms, allowing us to arrive at equation (7): {[HPDriving ÷ nDriving] × 63,025} ÷ {[HPDriven ÷ nDriven] × 63,025} = DDriving ÷ DDriven
Next week we’ll use equation (7) to link together R, N, n, of equation (1) with D and T of equation (2) and in so doing disclose mathematically the tradeoff between torque and speed, then apply our findings to an example. _______________________________________
|
Posts Tagged ‘forensic engineer’
Determining the Gear Train Tradeoff of Torque vs. Speed, Part One
Friday, August 15th, 2014The Gear Train Tradeoff
Tuesday, August 5th, 2014|
We’ve learned several methods to increase the torque of an electric motor through our series of articles on gear trains. One way is to attach a gear train to the motor’s shaft, a relatively simple thing to do. Today we’ll begin our exploration into how this method involves a tradeoff. It comes at the cost of speed. We’ll begin our examination of the tradeoff at play by linking together key elements learned through past blogs on the subject of gear trains. We’ll revisit those lessons through flashbacks. The first flashback we’ll make is to a blog entitled, Gear Ratio Formulas. There we learned that within a simple gear train consisting of two gears, the type most commonly employed to manipulate a motor’s torque, the ratio between the two gears, R, is relative to the ratio of their gear teeth, N. N is determined by the number of teeth each gear has in combination with the speeds, n, that each gear is going: R = NDriven ÷ NDriving = nDriving ÷ nDriven (1) The second flashback we’ll make is to a blog entitled, The Methodology Behind Gear Train Torque Conversions, in which we learned that the ratio of the torque, T, that exists between the gears is relative to the ratio of their respective pitch diameters, D: TDriving ÷ TDriven = DDriving ÷ DDriven (2) The tradeoff we’ve been alluding to comes in when gear speed, nDriven, represented in equation (1), is decreased, which results in an increase to TDriven in equation (2). But in order to see this we’ve got to somehow link the two equations together. In their present form there’s no common link between them. Or is there? There actually is an indirect link between the two equations, which comes by way of the torque equation presented in another past blog. The third flashback we’ll make is to the blog discussing that subject, which is entitled, The Relationship Between Torque and Horsepower. Using facts presented in that blog, the torque equations for our two gears become: TDriving = [HPDriving ÷ nDriving] × 63,025 (3) TDriven = [HPDriven ÷ nDriven] × 63,025 (4) Where’s the link between equations (1) and (2)? To answer that question we must reference a physics law known as The Law of Conservation of Energy . It states that the energy flowing from one gear to another within a gear train remains constant. Energy equates to horsepower, HP, in equations (3) and (4). So if the horsepower flowing through the gears is equal, our working equation becomes: HPDriving = HPDriven (5) Next time we’ll see how equation (5) is key to linking together equations (1) and (2) by way of equations (3) and (4). In so doing we’ll disclose the tradeoff to using gear trains. _______________________________________
|
Equations Used to Manipulate Torque Relative to Horsepower
Monday, July 28th, 2014|
Last time we learned that we can get more torque out of a motor by using one of two methods. In the first method we attach a gear train to the motor, then try different gear sizes until we arrive at the desired torque for the application. In the second method we eliminate the gear train altogether and simply use a higher horsepower motor to give us the torque we need. Today we’ll explore the second method. We’ll use the equation presented in our last blog to determine torque, T, relative to a motor’s horsepower, HP, when the motor operates at a speed, n: T = [HP ÷ n] × 63,025 In earlier blogs in this series we employed a gear train attached to an electric motor to power a lathe. It provided an insufficient 200 inch pounds of torque when 275 is required. Let’s use the equation and a little algebra to see how much horsepower this motor develops if it turns at a speed of 1750 RPM, a common speed for alternating current (AC) motors: 200 inch pounds = [HP ÷ 1750 RPM] × 63,025 200 = HP × 36.01 HP = 200 ÷ 36.01 = 5.55 horsepower For the purpose of our example today, let’s say we’ve nonsensically decided not to use a gear train, leaving us with no choice but to replace the underpowered motor with a more powerful one. So let’s see what size motor we’ll need to provide us with the required horsepower of 275 inch pounds. Using the torque equation and plugging in numbers already provided our equation becomes: 275 inch pounds = [HP ÷1750 RPM] × 63,025 275 = HP × 36.01 HP = 275 ÷ 36.01 = 7.64 horsepower This tells us that we need to replace the 5.55 horsepower motor with a 7.65 horsepower motor. As you might have guessed, the higher the motor’s horsepower, the larger that motor’s size and weight — if you’re not using a gear train, that is. Bigger, bulkier motors cost more to purchase and operate and also take up more space, which often makes them impractical to use. All this translates to the reality that sometimes it just makes more sense to use a gear train to provide more torque. It’s a lot easier and cheaper to attach a gear train to a motor and manipulate its gear sizes to arrive at desired torque than it is to buy a bigger motor. You may have deduced by now that it’s relatively easy to get more torque. Almost too easy. Next time we’ll see how increased torque comes at another type of cost, the cost of speed. _______________________________________
|
The Relationship Between Torque and Horsepower
Tuesday, July 15th, 2014| We’ve been discussing gear trains for some time now, and last time we posed the question: Why even bother using a gear train and performing complex computations to arrive at a desired torque for an application? Why not just use a bigger motor to start with? Today we’ll see why.
First, we must acknowledge that sometimes higher torque is achieved by simply using a more powerful motor. But sometimes this isn’t possible or practical. To begin our discussion, we must first understand how torque is related to motor power, the amount of mechanical work a motor can perform. Torque is in fact a function of how much mechanical power a motor produces. In the United States motor power is typically measured in units of horsepower. The following equation illustrates the relationship between torque, horsepower, and motor speed: T = [HP ÷ n] × 63,025 where T is the motor shaft’s torque in units of inch-pounds, HP is the motor’s horsepower, and n is the speed of the motor shaft in revolutions per minute (RPM). The number 63,025 in the equation is a constant used to convert the units of horsepower and RPM into units of torque (inch pounds). This equation applies to all sources of mechanical power. Its versatility enables design engineers to easily determine if a mechanical power source can deliver the torque required to drive a particular piece of machinery. The torque equation above tells us that in order to get a higher torque T for a given speed n, you’ll have to get a motor with a higher HP. Put another way, if your speed remains constant and you use a motor with higher horsepower, you’ll get more torque for your application simply by increasing the horsepower. Next time we’ll plug numbers into our equation and see how it all works. _______________________________________
|
How to Increase Gear Train Torque
Thursday, July 10th, 2014|
Last week we worked with a gear train equation and found that the gears under consideration were not sized properly to run a lathe. Today we’ll increase the gear train torque and solve that problem. How do we manipulate things to obtain the 275 inch pounds of torque required to drive the lathe? Last week we tried using a driven gear with a diameter of 8 inches and found that to be insufficient in size. So today the first thing we’ll try is a bigger driven gear, one with a pitch diameter of 8.5 inches. That’s 0.5 inches larger in diameter than the gear used in last week’s equation, and this just so happens to be the next size up in the gear manufacturer’s catalog. As we did last week, we’ll begin our calculations with the torque ratio equation: T1 ÷ T2 = D1 ÷ D2 We’ll use the same values as last week for T1, and D1, 200 inch pounds and 3 inches respectively, but we’ll increase the new value for D2, the driven gear pitch radius, to 4.25 inches (the new pitch diameter divided by two). Inserting these values into the torque equation, the only variable remaining without a value is torque T2. Let’s determine that value now by using algebra to rearrange terms. (200 inch pounds) ÷ T2 = (3 inches) ÷ (4.25 inches) (200 inch pounds) ÷ T2 = 0.70 T2 = (200 inch pounds) ÷ (0.70) = 283.33 inch pounds The value of T2 is found to be 283.33 inch pounds, which meets the torque requirement required to run the lathe. We were able to arrive at this torque by simply increasing the size of the driven gear relative to the size of the driving gear. In the world of Newtonian physics, this is a rather straightforward arrangement. It all boils down to this simple dynamic: When the motor’s force is acting upon a wider gear, the force is located a longer distance from the center of the driving gear shaft, which results in more torque on the shaft. As borne out by the example provided today, the larger the driven gear is in comparison to the driving gear, the more the gear train amplifies the torque that’s delivered by the motor. The principle at play here is exactly the same as that presented in a previous blog article where, for a given force exerted upon a wrench, torque was increased by simply increasing the length of the wrench handle. Some of you may be wondering why we didn’t just use a bigger, more powerful motor to begin with, thereby eliminating the need for a gear train and all the calculations we’ve been running? We’ll see why that’s not always possible or practical next time. _______________________________________
|
The Methodology Behind Gear Train Torque Conversions
Sunday, June 22nd, 2014|
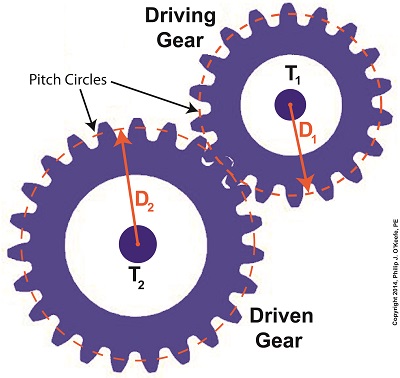
Last time we learned that gear trains are torque converters, and we developed a torque ratio equation which mathematically ties the two gears in a gear train together. That equation is: T1 ÷ T2 = D1 ÷ D2 Engineers typically use this equation knowing only the value for T2, the torque required to properly drive a piece of machinery. That knowledge is acquired through trial testing during the developmental phase of manufacturing. Once T2 is known, a stock motor is selected from a catalog with a torque value T1 which closely approximates that of the required torque, T2. Then calculations are performed and lab tests are run to determine the driving and driven gear sizes, D1 and D2 which will enable the gear train to convert T1 into the required value of T2. This series of operations are often a time consuming and complex process. To simplify things for the purpose of our example, we’ll say we’ve been provided with all values required for our equation, except one, the value of T2. In other words, we’ll be doing things in a somewhat reverse order, because our objective is simply to see how a gear train converts a known torque T1 into a higher torque T2. We’ll begin by considering the gear train illustration above. For our purposes it’s situated between an electric motor and the lathe it’s powering. The motor exerts a torque of 200 inch pounds upon the driving gear shaft of the lathe, a torque value that’s typical for a mid sized motor of about 5 horsepower. As-is, this motor is unable to properly drive the lathe, which is being used to cut steel bars. We know this because lab testing has shown that the lathe requires at least 275 inch pounds of torque in order to operate properly. Will the gears on our gear train be able to provide the required torque? We’ll find out next time when we insert values into our equation and run calculations. _______________________________________
|
Gear Trains Are Torque Converters and Why That’s Important
Friday, June 13th, 2014|
Today we’ll analyze the relationship between the sizes of the gears within a gear train, as well as their torques, and get an understanding of how gear trains act as torque converters. Last time we developed a single torque equation for a simple gear train: T1 ÷ D1 = T2 ÷ D2 (1) where T1 and T2 are the driving and driven gear torques, and D1 and D2 are the driving and driven gear pitch circle radii. The first thing to be done in order to arrive at a torque conversion analysis is group together like terms in equation (1) so that we end up with terms relating to torque on one side of the equation and terms relating to gear size on the other. We’ll use algebra to divide both sides of the equation by T2 , then multiply both sides by D1. After doing so we get, T1 ÷ T2 = D1 ÷ D2 (2) In equation (2), T1 ÷ T2 is a torque ratio. Ratio means we’re dividing one of the torques by the other. Likewise, D1 ÷ D2 is a gear pitch radius ratio, that is to say, it’s the ratio of one gear’s physical size relative to the physical size of the other. What equation (2) tells us is that the individual gears on the gear train will produce torque values which are dependent upon the physical sizes of the two gears with respect to one another. So what’s the practical significance of this? When gear trains are used in industrial applications, they always act as torque converters. One such example would be when a low-torque-producing electric motor is used to power a steel cutting lathe. If the motor isn’t tough enough to power the lathe, it itself won’t be modified, but the torque it produces will be. This modification is accomplished by converting the motor’s low torque value, T1, to a higher torque value, T2 , and it’s equation (2) that’s used to do it. Next time we’ll delve deeper into the methodology behind gear train torque conversions. _______________________________________
|
Equating Torques and Pitch Circle Radii Within a Gear Train
Thursday, May 29th, 2014|
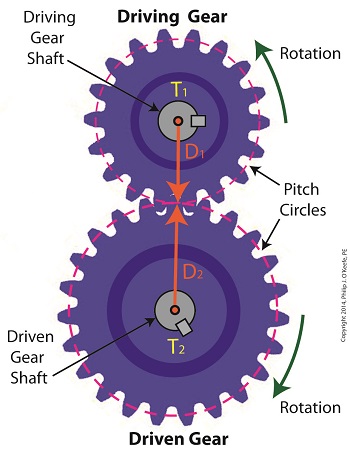
Last time we developed torque equations for the driving and driven gears within a simple gear train. They are, T1 = D1 × F T2 = D2 × F where, T1 and T2 are the driving and driven gear torques, D1 and D2 are the driving and driven gear pitch radii, and F is the resultant Force vector, the common factor between the two equations. Now we’ll combine these two equations relative to F to arrive at a single equation which equates the torques and pitch circle radii of the driving and driven gears in the gear train. This type of computation is commonly used to design gear trains to ensure they perform at a given level. As a first step we’ll use algebra to rearrange terms and place the two equations equal to F. First we’ll do it for the driving gear, dividing both sides of the equation by the pitch circle radius, D1. T1 ÷ D1 = D1 ÷ D1 × F T1 ÷ D1= 1 × F F = T1 ÷ D1 In a similar fashion, we’ll do it for the driven gear by dividing both sides of the equation by the pitch circle radius, D2. T2 = D2 × F → F = T2 ÷ D2 Since F is the common term between the two equations, we can set them up as equal to each other, F = T1 ÷ D1 = T2 ÷ D2 which means that, T1 ÷ D1 = T2 ÷ D2 Next time we’ll see how to use this equation to manipulate our gear train so that it acts as a torque converter by increasing T2 with respect to T1 and the ratio of D1 to D2, thus providing a mechanical advantage to the electric motor the gear train is attached to. _______________________________________ |
Gear Train Torque Equations
Thursday, May 22nd, 2014|
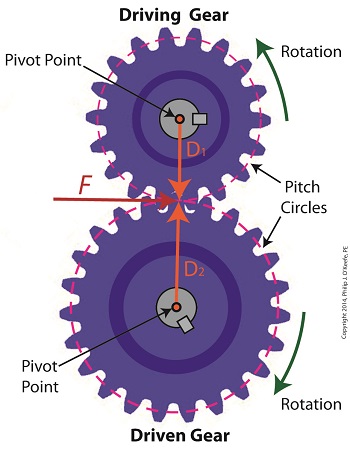
In our last blog we mathematically linked the driving and driven gear Force vectors to arrive at a single common vector F, known as the resultant Force vector. This simplification allows us to achieve common ground between F and the two Distance vectors of our driving and driven gears, represented as D1 and D2. We can then use this commonality to develop individual torque equations for both gears in the train. In this illustration we clearly see that the Force vector, F, is at a 90º angle to the two Distance vectors, D1 and D2. Let’s see why this angular relationship between them is crucial to the development of torque calculations. First a review of the basic torque formula, presented in a previous blog, Torque = Distance × Force × sin(ϴ) By inserting D1, F, and ϴ = 90º into this formula we arrive at the torque calculation, T1 , for the driving gear in our gear train: T1 = D1 × F × sin(90º) From a previous blog in this series we know that sin(90º) = 1, so it becomes, T1 = D1 × F By inserting D2, F, and ϴ = 90º into the torque formula, we arrive at the torque calculation, T2 , for the driven gear: T2 = D2 × F × sin(90º) T2 = D2 × F × 1 T2 = D2 × F Next week we’ll combine these two equations relative to F, the common link between them, and obtain a single equation equating the torques and pitch circle radii of the driving and driven gears in the gear train. _______________________________________ |
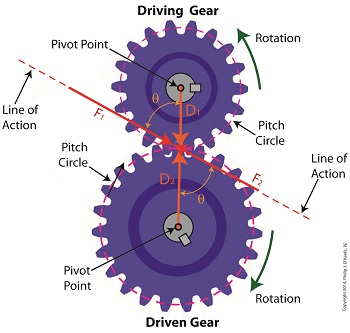
The Mathematical Link Between Gears in a Gear Train
Wednesday, May 14th, 2014|
Last time we analyzed the angular relationship between the Force and Distance vectors in this simple gear train. Today we’ll discover a commonality between the two gears in this train which will later enable us to develop individual torque calculations for them. From the illustration it’s clear that the driving gear is mechanically linked to the driven gear by their teeth. Because they’re linked, force, and hence torque, is transmitted by way of the driving gear to the driven gear. Knowing this we can develop a mathematical equation to link the driving gear Force vector F1 to the driven gear Force vector F2, then use that linking equation to develop a separate torque formula for each of the gears in the train. We learned in the previous blog in this series that F1 and F2 travel in opposite directions to each other along the same line of action. As such, both of these Force vectors are situated in the same way so that they are each at an angle value ϴ with respect to their Distance vectors D1 and D2. This fact allows us to build an equation with like terms, and that in turn allows us to use trigonometry to link the two force vectors into a single equation: F = [F1 × sin(ϴ)] – [F2 × sin(ϴ)] where F is called a resultant Force vector, so named because it represents the force that results when the dead, or inert, weight that’s present in the resisting force F2 cancels out some of the positive force of F1. Next week we’ll simplify our gear train illustration and delve into more math in order to develop separate torque computations for each gear in the train. _______________________________________ |